12.1.2 Engine starting
ENGINE WAS STARTED, IT IS WORKING PROPERLY
- Before starting the engine, it is necessary to establish the selector lever of a transmission (automatic) in position "P" or position "N" in case if transmission is mechanical.
- It is necessary to check the working capacity of the vacuum booster of brake system. Press the brake pedal and start the engine. In case if with the brake pedal moving slightly under the force of the foot - this will mean that the vacuum booster is functioning normally. In case if at start the brake pedal did not move, it is recommended to contact the service station for more detailed diagnostics of the car.
- Modern cars are equipped with electronic control units (ECU), therefore at start-up there is no need to keep the accelerator pedal pressed. The electronics will automatically increase engine speed for faster warm-up, then will lower it to normal idle speed.
- At start-up some alarms of separate systems of the car light up. At this moment selfdiagnostics of these systems is performed. After some seconds alarms have to go out. In case if any signaling indicator does not go out, it is necessary to consult the section "Car Operation" given in this manual or contact the service station.
- In the winter for cars with a manual transmission in order to simplify engine start it is necessary to press a clutch pedal. In case of a diesel engine the car may be equipped with a pre-heating system. This system is switched on automatically before engine start, and a special signaling indicator lights up. Engine can be started after that.
- After successful start of the engine it is desirable to open a hood and to look over all basic elements of the engine in order to be convinced of leaks on the main connections (cylinder heads, sump and engine block, a transmission and the engine) and brake fluids in the expansion tanks. In case if it is necessary refill them to the required level.
- It is necessary to check the operation of all elements of the lighting system:
- headlights (low beam/high beam/fog lights);
- turn indicators and their repeaters (front and rear);
- rear brake lights, rear fog lights and car reversing lights.
ENGINE DOES NOT START, CRANKSHAFT DOES NOT ROTATE
- Check the battery pack charge level.
- Check that the wiring terminals are properly connected to the battery pack. Additionally, check the wiring terminals for oxidation (clean the terminals if necessary).
- Check the connection of high-voltage wires of spark plugs, check a wire/wires of the coil/ignition coils.
- Check the starting system fuses.
- Check the connection of electric wiring to a starter of starting system.
- Check a technical condition of spark plugs.
- Check ignition system fuses.
- Using a density gage, measure the density of the electrolyte in each bank of the battery (see chapter "Engine Electrical Equipment").
- Using a voltmeter, measure the voltage at the terminals of the battery pack.
- Check the technical condition of the starter.
ENGINE DOES NOT START, CRANKSHAFT ROTATES
- Check the fuel level in the fuel tank. Be careful and cautious, because some models are equipped with electric fuel pumps, that are lubricated with its own fuel. Thus, in case of full fuel consumption the pump will run "dry", which can lead to its breakdown. Besides that, it is necessary to consider that the lamp of the signaling device of low level of fuel lights up if there are 5-8 liters of fuel in a tank.
- Check that the wiring terminals are properly connected to the battery pack. Also check the wiring terminals for oxidation (clean the terminals if necessary). In case if the terminals are oxidized, the crankshaft may turn very slowly and stop.
- A situation is possible when the engine "picks up" (starts, rotates a few turns and stops). The cause may be air suction in one of the elements of the intake system. Air suction is possible from the following interfaces of elements of system of intake:
- place of fastening of a throttle valve body to an air duct (towards an intake manifold);
- place of fastening of an air duct to an intake manifold;
- connection of intake manifold with the cylinder head;
- suction is possible on some cars because of loose fastening of the sensor of temperature of intake air.
- Check the state of engine control system sensors. Modern engine control systems are equipped with many sensors that read information about certain parameters of a mechanism or system and send signals to the electronic control unit (ECU/ECM/PCM) - all this is done for optimization and improving the engine performance. But there are sensors that in case of failure will indirectly affect work (fuel consumption will change and / or power will decrease, there will be any interruptions in work, etc.). Thus, the engine will continue working. «CHECK ENGINE»
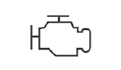 signalingindicator will light up on the instrument panel. In addition, there are several basic sensors, in case of failure of which the engine will not start, namely:
signalingindicator will light up on the instrument panel. In addition, there are several basic sensors, in case of failure of which the engine will not start, namely:
- Excess oxygen sensor (lambda probe).
On modern cars it is installed before and after the catalytic converter. - Crankshaft position sensor.
It is installed either in the front part of the engine, or in back, over a flywheel. - Mass air flow sensor. It is installed in the air duct of the intake system in front of the
throttle valve.
- Excess oxygen sensor (lambda probe).
- In the winter (during the first morning start after a night in the garage or on a parking lot) it is possible that the crankshaft will rotate very slowly, not enough to start the engine. Freezing
of the battery pack may be the reason. In order to warm up the battery pack, it is necessary to turn on the high beam of the headlights for 1-2 minutes, then try to start the engine again. In case if the engine does not start, check for possible causes above. On cars with a diesel engine, the possible cause may be the formation of paraffin plugs in the fuel lines and fuel channels (such a violation is typical for cars that are idle for a long time in an unheated parking lot).
- In case if the car was standing in the open parking lot at night in the winter, the difficult start is possible due to thickening of engine and transmission oils.
ENGINE STARTS, BUT WORKS WITH INTERRUPTIONS
- Malfunctioning of the fuel system. Causes of this malfunction may be a malfunction of the fuel pump (high pressure fuel pump - for diesel engines), air inside of fuel lines, contamination of fuel injector nozzles, heavy soot on the injector nozzles (diesel engines). All the work that are related to fuel system elements shall be performed at specialized service stations.
- Air suction in one of the elements of the intake system may be the reason. Air suction is possible from the following connections of elements of intake system:
- place of fastening of a throttle valve body to an air duct (towards an intake manifold);
- place of fastening of an air duct to an intake manifold;
- connection of intake manifold with cylinder head.
3а. Ignition system malfunctions (gasoline engines only). At the same time works that are connected with elements of ignition system shall be done at specialized service stations. You can check the following on your own:
- correct connection of high-voltage wires: they shall be mounted tightly on the tips of the spark plugs and on the ignition coils;
- technical condition of spark plugs and conformity of the established spark plugs to technical requirements of the automaker You can also use the soot or deposits on the spark plug electrodes for determining which engine malfunctions have occurred;
Note
There are two main types of spark plugs: hot and cold.
- check the quality of the fuel to be filled.
3b. Fault in the operation of the HPFP (high pressure fuel pump), which is associated with a shift in the start and change in the duration of the fuel injection. The reason may be the displacement of the drive sprockets of this pump (provided that the pump was removed and installed) relative to the drive chain or belt.
4. Wrong installation of phases of gas distribution. At the same time operation of the engine can proceed, but with the increased fuel consumption and big loss of power. There are many reasons that can lead to such a fault, but there are two main ones:
- while replacing the drive chain/timing belt (gas distributing mechanism) there was a phase shift;
- malfunctions of the engine electronic control unit (ECU).
Note
It is recommended to eliminate the specified malfunctions on a service station.
- Wrong ignition advance angle setting (see chapter 4 "Engine"). In case if the ignition advance angle was shifted to a later value, engine interruptions may be accompanied by cracks in the car's exhaust system, as well as the presence of black smoke from the exhaust pipe. In this case, the engine shall be stopped as soon as possible, because unburned fuel inside the cylinders will burn out in the catalytic converter, which can lead to its failure. In case if, on the other hand, the intake manifold claps during engine interruptions at idle speed, this indicates a shift of the angle to the zone of earlier ignition. Failure to set the ignition advance angle can have serious consequences that can result from overloading of individual engine components, assemblies and systems.
- Malfunctions in the charging system. At the same time after engine start the signaling indicator of lack of charging of the battery pack
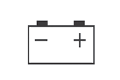 will light up on the instrument panel in the passenger compartment. In this case, it is necessary to check the points of connection of the wiring to the generator. In case if the wiring is connected properly, then contact the service station to determine the cause of the fault.
will light up on the instrument panel in the passenger compartment. In this case, it is necessary to check the points of connection of the wiring to the generator. In case if the wiring is connected properly, then contact the service station to determine the cause of the fault. - In case if there is a gray smoke coming out of the exhaust pipe when the engine is running, the cause may be engine oil entering the cylinders (through valve bushings or piston rings). This causes soot on the pistons, spark plugs and injectors, causing the engine to start work with interruptions. In this case, it is necessary to contact the service station in order to perform repair works.
For diesel engines
In case if black smoke comes out of the exhaust pipe and the engine runs with interruptions, the cause may be a leaky closure of the injector nozzle with a valve, which leads to fuel leaks into the cylinder.
8. Engine malfunction may occur due to reduced compression inside one or more engine cylinders.















2 MB