6.2.9 Tire tread patterns
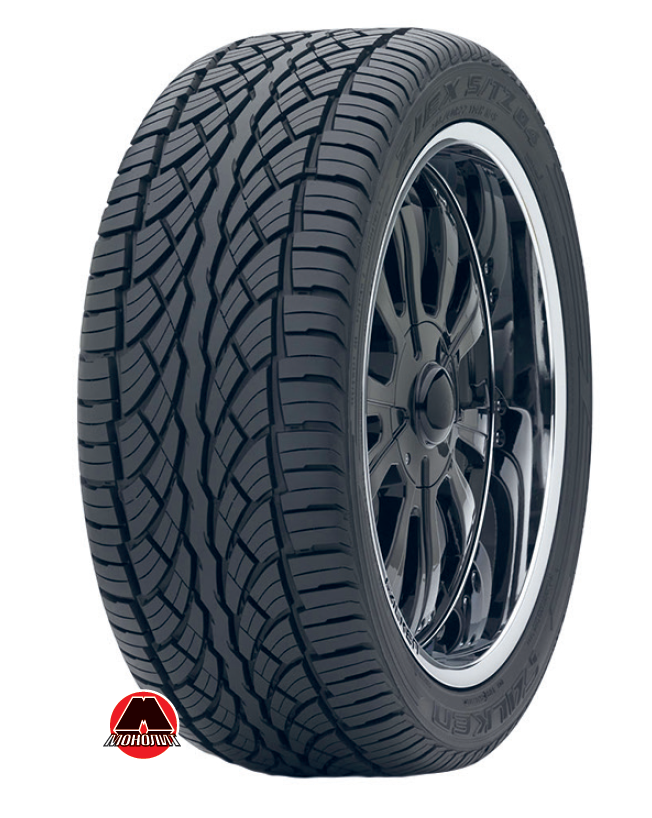
- Non-directional (Figure 6.22) is a pattern, which is symmetrical about the vertical axis of the wheel passing through its axis of rotation. It is the most versatile, which is why most of the tires are produced with this pattern.
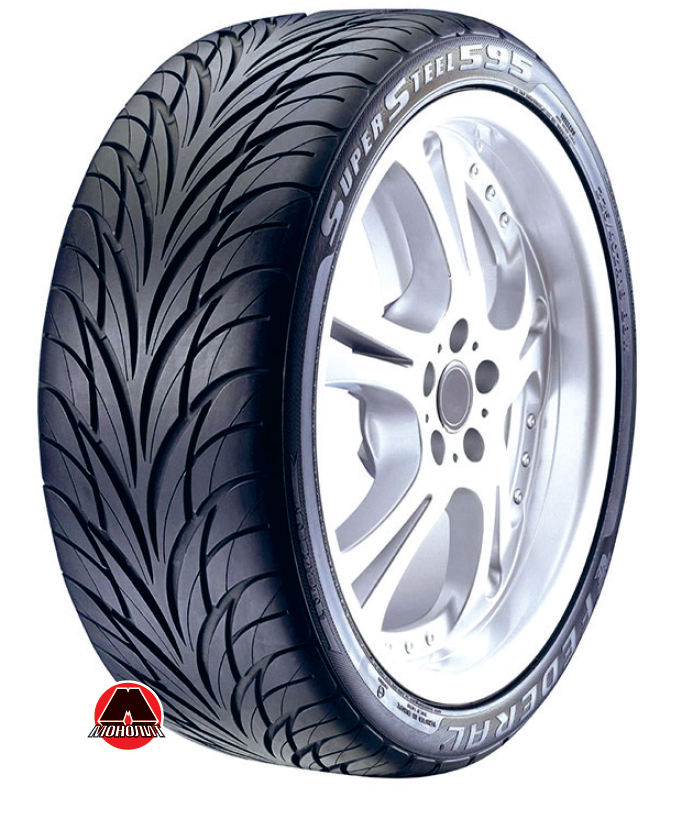
- Uni-directional (Figure 6.23) is a pattern, which is symmetrical with respect to the vertical axis passing through the central part of the tread. Its benefits include improved ability to drain water from the road contact patch and lower noise levels.
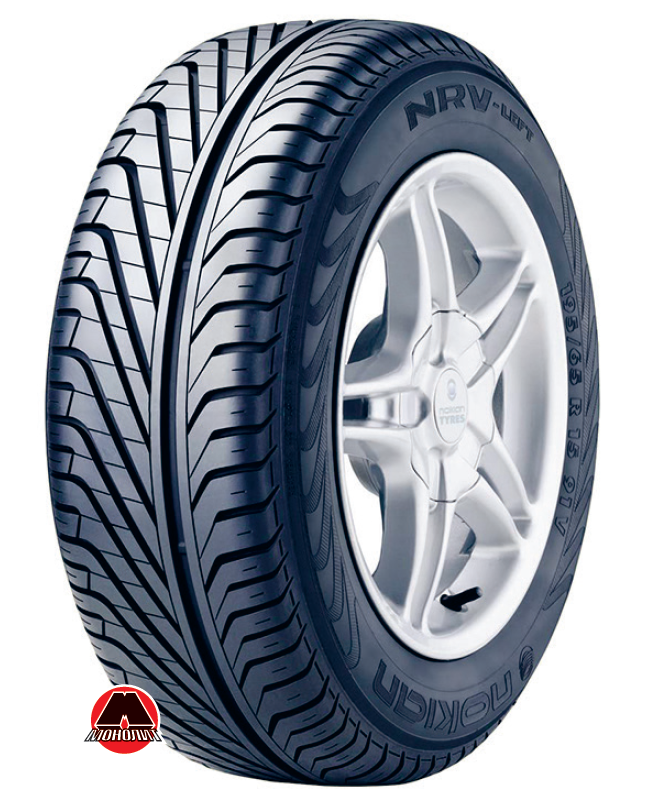
- Asymmetrical (Figure 6.24) is a pattern, which is asymmetrical about the vertical axis of the wheel. It is used for the implementation of various properties in one tire. For example, the outside of a tire performs better on dry roads, while the inside performs better on wet surfaces.
|
Figure 6.22 Example of tire with non-directional type tread pattern. |
Figure 6.23 Example of tire with unidirectional tread pattern. |
Figure 6.24 Example of tire with asymmetrical tread pattern. |


















2 MB